AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 是一个非常重要的后置处理器,主要用于为 bean 填充属性。
类图如下:
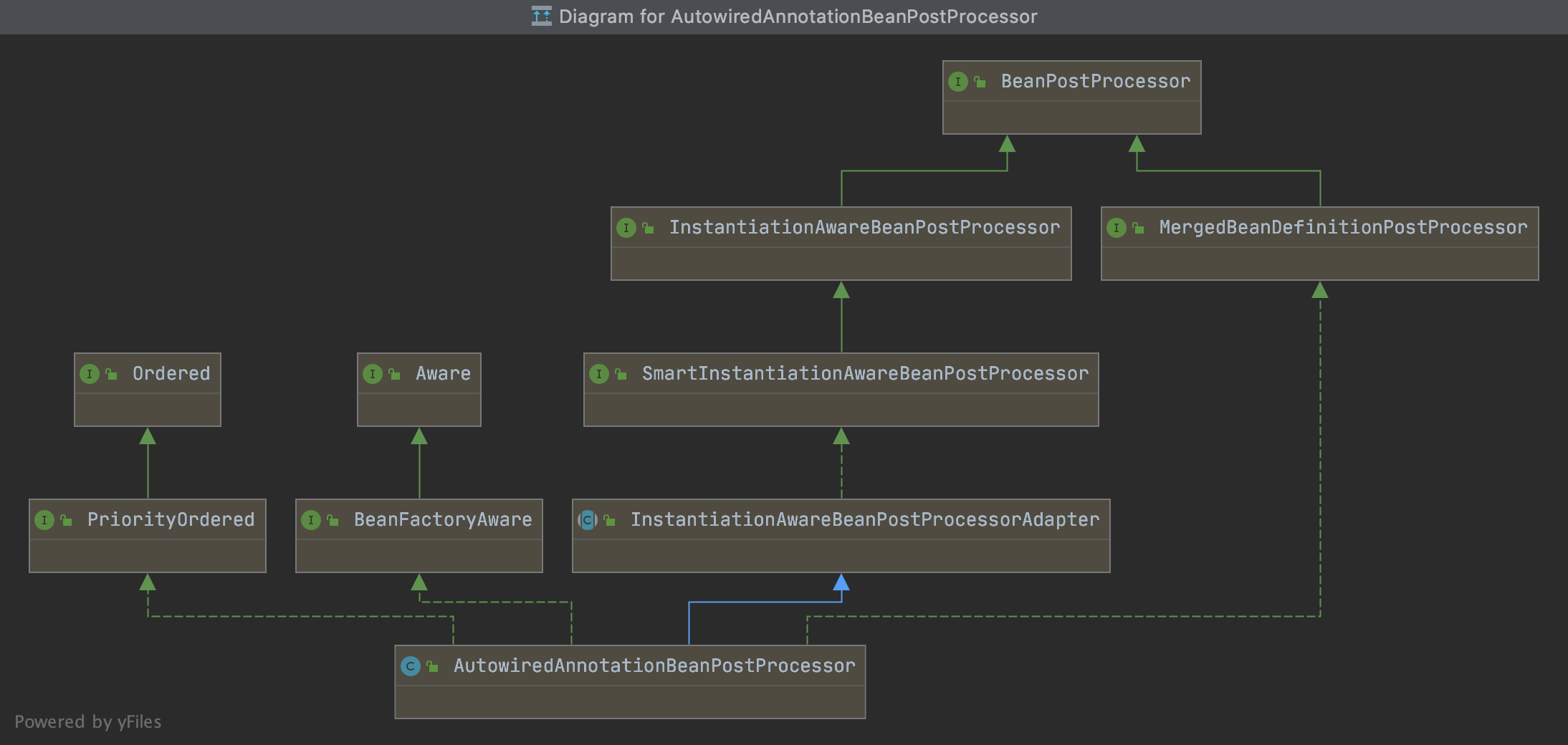
该处理器实现了 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 接口,最重要的就是 postProcessProperties 方法,用于填充 bean 的属性。
构造器
该类只有一个构造方法,该方法设置了 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 能够支持哪些注解,默认有 Autowired、Value、和 Inject, Inject 则是 JSR-330 的标准。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Autowired.class);
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Value.class);
try {
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>)
ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Inject", AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader()));
logger.trace("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Inject' annotation found and supported for autowiring");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
}
}
|
依赖注入 populateBean 方法调用的主入口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
|
寻找需要自动装配的元数据
简而言之,就是先尝试从缓存拿,拿不到就去构建,构建完再放入缓存。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
|
构建需要自动装配的元数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
| private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
@Nullable
private MergedAnnotation<?> findAutowiredAnnotation(AccessibleObject ao) {
MergedAnnotations annotations = MergedAnnotations.from(ao);
for (Class<? extends Annotation> type : this.autowiredAnnotationTypes) {
MergedAnnotation<?> annotation = annotations.get(type);
if (annotation.isPresent()) {
return annotation;
}
}
return null;
}
|
注入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
|
按属性注入
流程很清晰,就是获取依赖的 bean,用反射赋值给属性。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| private class AutowiredFieldElement extends InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement {
private final boolean required;
private volatile boolean cached = false;
@Nullable
private volatile Object cachedFieldValue;
public AutowiredFieldElement(Field field, boolean required) {
super(field, null);
this.required = required;
}
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
else {
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
try {
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
if (value != null || this.required) {
this.cachedFieldValue = desc;
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
this.cachedFieldValue = new AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
}
}
}
else {
this.cachedFieldValue = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (value != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
}
|
按方法注入
也就是常说的 set注入。
流程也比较清晰,找到方法上的所有参数,依次获取 bean,最后把所有参数传进去,反射调用对象的方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
Method method = (Method) this.member;
Object[] arguments;
if (this.cached) {
// Shortcut for avoiding synchronization...
arguments = resolveCachedArguments(beanName);
}
else {
int argumentCount = method.getParameterCount();
arguments = new Object[argumentCount];
DependencyDescriptor[] descriptors = new DependencyDescriptor[argumentCount];
Set<String> autowiredBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(argumentCount);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
for (int i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
MethodParameter methodParam = new MethodParameter(method, i);
DependencyDescriptor currDesc = new DependencyDescriptor(methodParam, this.required);
currDesc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
descriptors[i] = currDesc;
try {
// 依次解析依赖
Object arg = beanFactory.resolveDependency(currDesc, beanName, autowiredBeans, typeConverter);
if (arg == null && !this.required) {
arguments = null;
break;
}
arguments[i] = arg;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(methodParam), ex);
}
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
if (arguments != null) {
DependencyDescriptor[] cachedMethodArguments = Arrays.copyOf(descriptors, arguments.length);
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeans);
if (autowiredBeans.size() == argumentCount) {
Iterator<String> it = autowiredBeans.iterator();
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < paramTypes.length; i++) {
String autowiredBeanName = it.next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, paramTypes[i])) {
cachedMethodArguments[i] = new AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
descriptors[i], autowiredBeanName, paramTypes[i]);
}
}
}
this.cachedMethodArguments = cachedMethodArguments;
}
else {
this.cachedMethodArguments = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (arguments != null) {
try {
// 反射调用方法
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(bean, arguments);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
|
